Our brains communicate with electrical and Deborah Driggs Archiveschemical signaling, but scientists have discovered that light stimulation could hold potential keys to manipulating neuronal communication pathways that influence motor control, sensory perception, memory, neurochemical production and mood – or cellular virtual reality, as a report from the Journal of Cell Biology describes it.
With the roll out of the White House's $300 million BRAIN Initiative in 2013, interest in uncovering the secrets of the human brain has accelerated and now includes many government agencies, public/private partnerships and universities.
Dating back to at least 1971, optogenetic research has matured enough to gain the attention of organizations such as the NIH, DARPA and IARPA, who are exploring the role that light-sensitive cells could soon play in fields surrounding neurobiological, including physical and mental health, human-machine interfacing, and advancing artificial intelligence through reverse brain engineering.
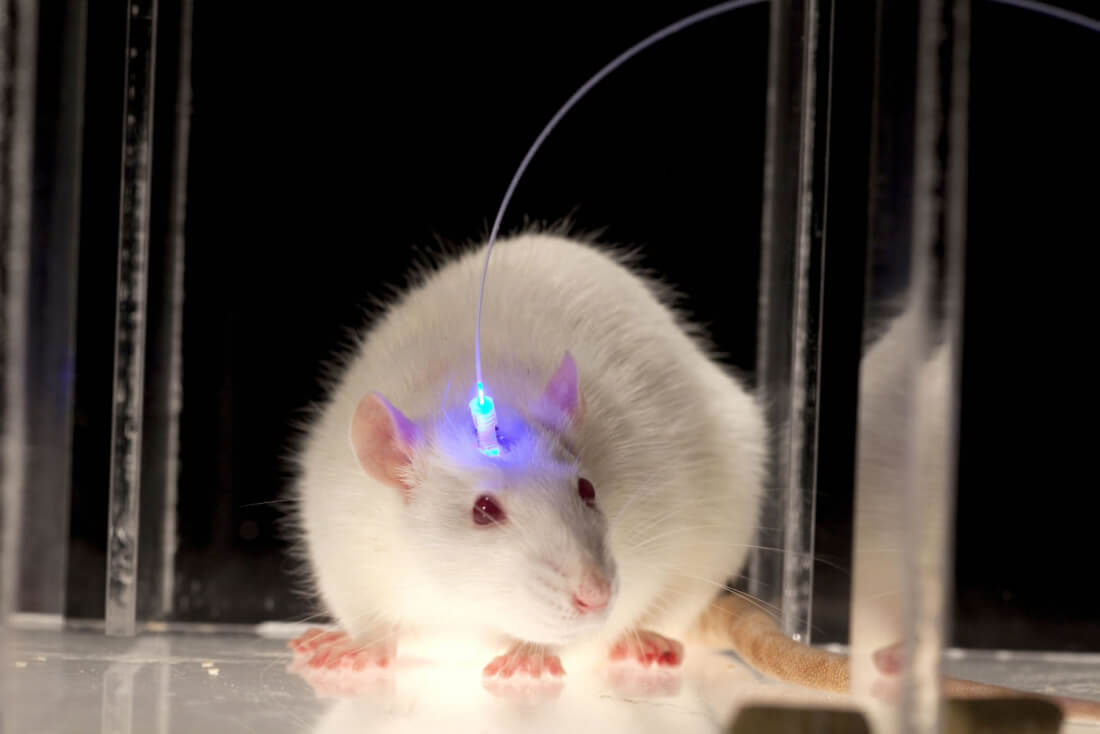
Current optogenetic experiments rely on extracting "opsins" (light-sensitive proteins) from plants which can be introduced to mammals by methods including injection and infection via adenovirus.
Once delivered into an organism, opsins can be expressed in eye, brain or skin cells, allowing their light-sensitivity to be remotely activated or silenced with timed pulses of light in different color wavelengths across the light spectrum that can target multiple bodily systems and cause a variety of biological effects.
Researchers have suggested however that introducing opsins into an organism may not be a long-term requirement as methods are sought for using optogenetics on mammalian cells that respond naturally to light, such as those in the human retina.
As part of the BRAIN Initiative, scientists have been working on neuronal barcoding and completing a detailed online brain atlas for researchers. This is hoped to eventually provide a detailed circuit diagram of every neuron and synapse in the brain, which would allow various neuronal patterns to be identified so they can be triggered for the desired effect.
If targeted precisely enough with the appropriate light, it's thought that optogenetics could be used by manipulating neural circuits involved with pain, fear, reward, wakefulness and social behaviors. In one Yale study, for example, mice were infected with a virus which made their neurons sensitive to blue light. Scientists then used that light pathway to activate predatory behavior.
"...The researchers used a tiny optic fibre to shine a blue laser on the amygdala. This prompted the animals to tense their jaw and neck muscles... 'It's not just physiological, it's hunting, biting, releasing and eating. Those are motor sequences that require a lot of information...' [said an MIT neuroscientist]"
In 2015, optogenetics was combined with CRISPR to develop a set of photoactivatable tools that enable the editing of an organism's genome through the external use of light. Said tools can control the location, timing and reversibility of the genome editing process, whether that be activating, repressing or modifying a gene.
Optogenetics is also mentioned as an integral feature of the DARPA-funded Neural Engineering System Design (NESD) program, a joint effort between six teams who are aiming to create an implantable neural interface over the next four years that is capable of high resolution brain-to-machine communication. Such advancements, for instance, could facilitate the development of mind-controlled prosthetics featuring touch sensation like the DARPA-backed 'Luke' arm (previously known as the 'Deka' arm).
In the past, DARPA has looked to optogenetic memory manipulation techniques for treating veterans with traumatic brain injury and/or PTSD through memory restoration or deletion.
More recently, during a November 2017 mental health conference with 30,000 attendees in Washington D.C., optogenetics was noted for the impact it's having on the ability to study the brain. According NPR science correspondent Jon Hamilton, the technology has allowed aspects of human mental health disorders to be reproduced in animals, aiding the mapping of neuronal circuits involved with issues such as depression.
Companies interested in the application of optogenetic technologies have begun emerging over the last decade, particularly since the FDA approved the technology in 2015 for use in treating an eye disorder known as "retinitis pigmentosa."
The approval prompted a clinical trial and optogenetic developments have since been used to restore partial vision in patients who were described as being "profoundly blind." Chronic pain management, epilepsy and Parkinson's are among many health issues that researchers are experimenting with addressing through optogenetics.
The technology is also contributing to other areas of research such as "sonogenetics," which uses low-pressure ultrasound to activate ultrasonically sensitized neurons. This is another area of interest for DARPA, which has funded Columbia University's endeavor to stimulate neurons using ultrasound and believes it could eventually lead to a magnetic version of the technology called "magnetogenetics."
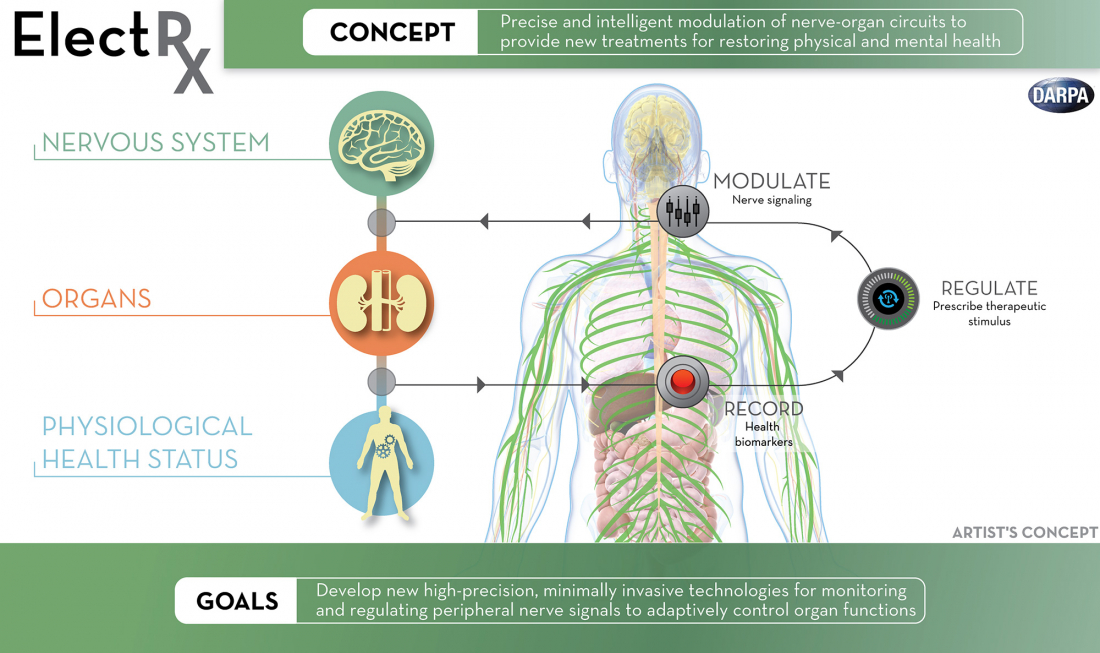
To investigate the therapeutic use of optogenetics, acoustics and electromagnetic fields, DARPA launched the ElectRX (Electrical Prescription) program in 2015, which is capable of stimulating, modulating and monitoring the body's peripheral nervous system. The research agency is also exploring how artificial intelligence could be used in closed-loop brain implants, such as the ability to detect patterns associated with mood disorders.
With enough progress, it's believed that optogenetics and its surrounding bodies of research may open the door to real-time brain mapping and biofeedback technologies, which could be used to treat all manner of ailments on the fly through closed-loop neuromodulation signals coming to and from an implanted device, ultimately eliminating the need for pharmaceuticals.
 The Baffler’s May Day Round Up
The Baffler’s May Day Round Up
 Surface Noise: What We’ve Lost in the Transition to Digital
Surface Noise: What We’ve Lost in the Transition to Digital
 Five Short Stories from “The Teeth of the Comb”
Five Short Stories from “The Teeth of the Comb”
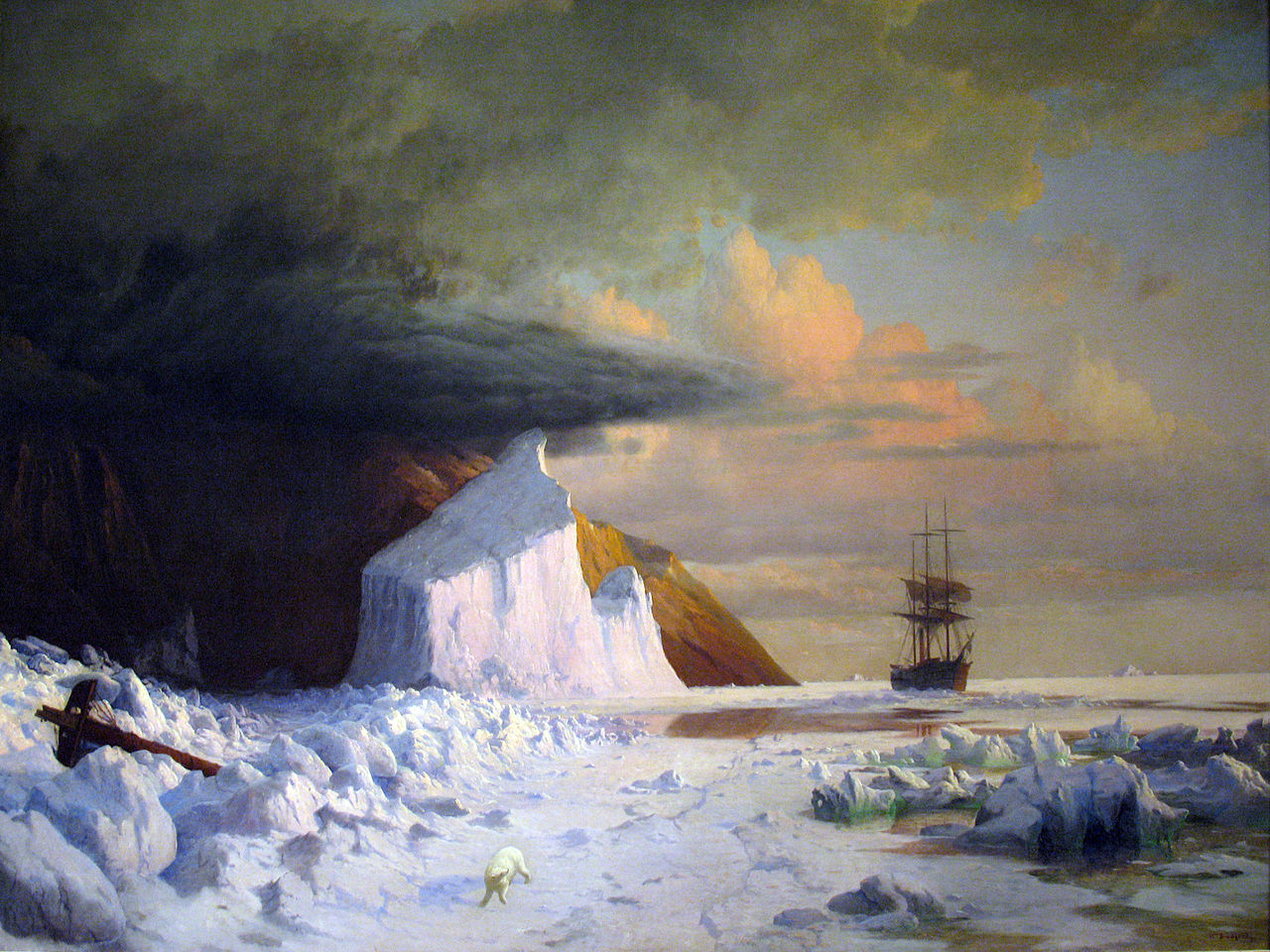 The Victorian Fantasy of the North Pole Was the Opposite of Ours
The Victorian Fantasy of the North Pole Was the Opposite of Ours
 Operation Rock Wallaby rains food down on wildlife hurt by bushfires
Operation Rock Wallaby rains food down on wildlife hurt by bushfires
 Omegle changed cybersex forever, for better or worse
Omegle changed cybersex forever, for better or worse
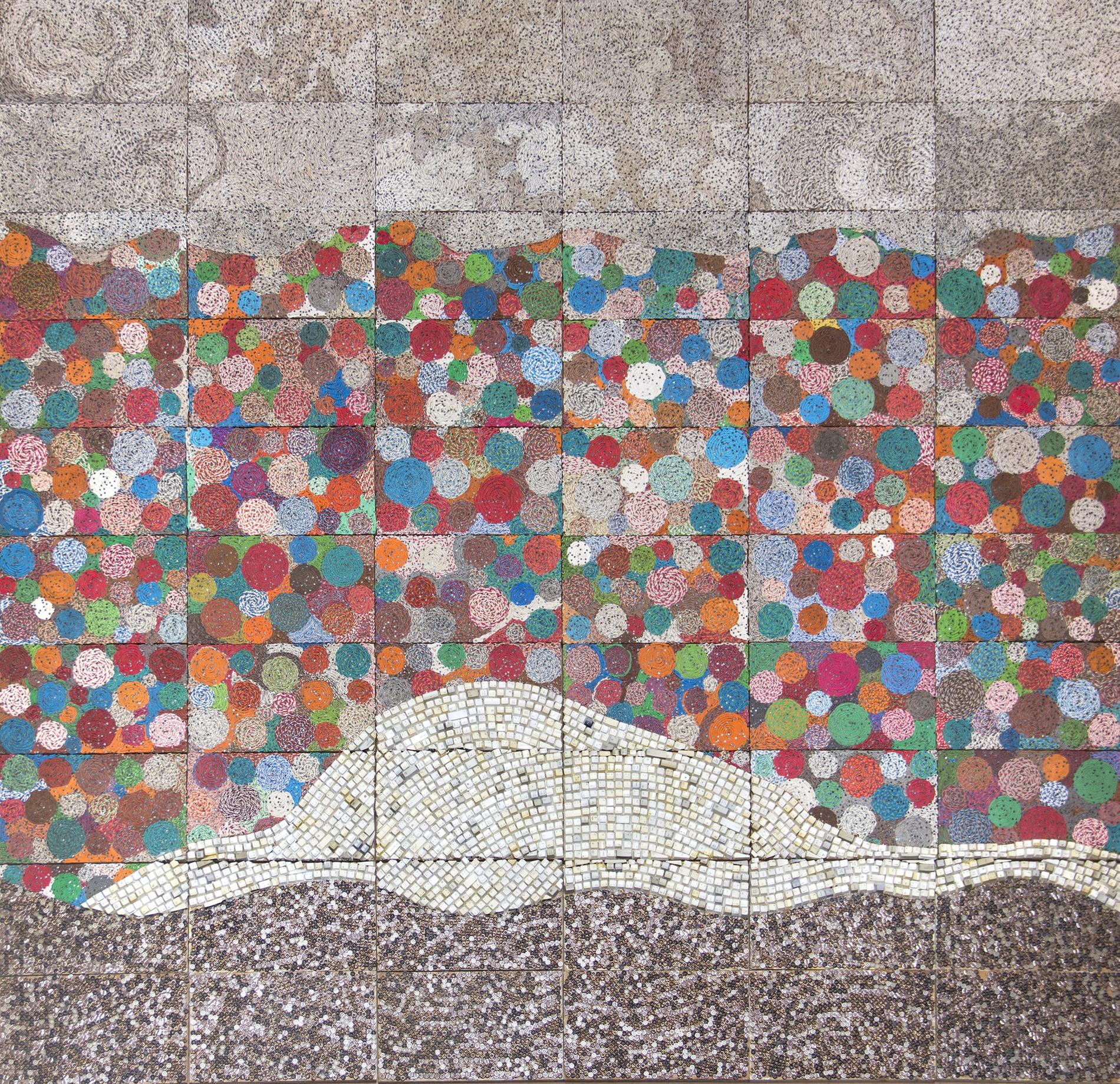 Elias Sime’s Art Repurposes Electronic Waste from Abbis Ababa
Elias Sime’s Art Repurposes Electronic Waste from Abbis Ababa
 Major ChatGPT outage due to DDoS attack
Major ChatGPT outage due to DDoS attack
 Alienware M16 Gaming Laptop deal: Save $560
Alienware M16 Gaming Laptop deal: Save $560
 Meta announces 'The Notorious B.I.G. Sky's The Limit: A VR Concert Experience'
Meta announces 'The Notorious B.I.G. Sky's The Limit: A VR Concert Experience'
 The Baffler’s May Day Round Up
The Baffler’s May Day Round Up
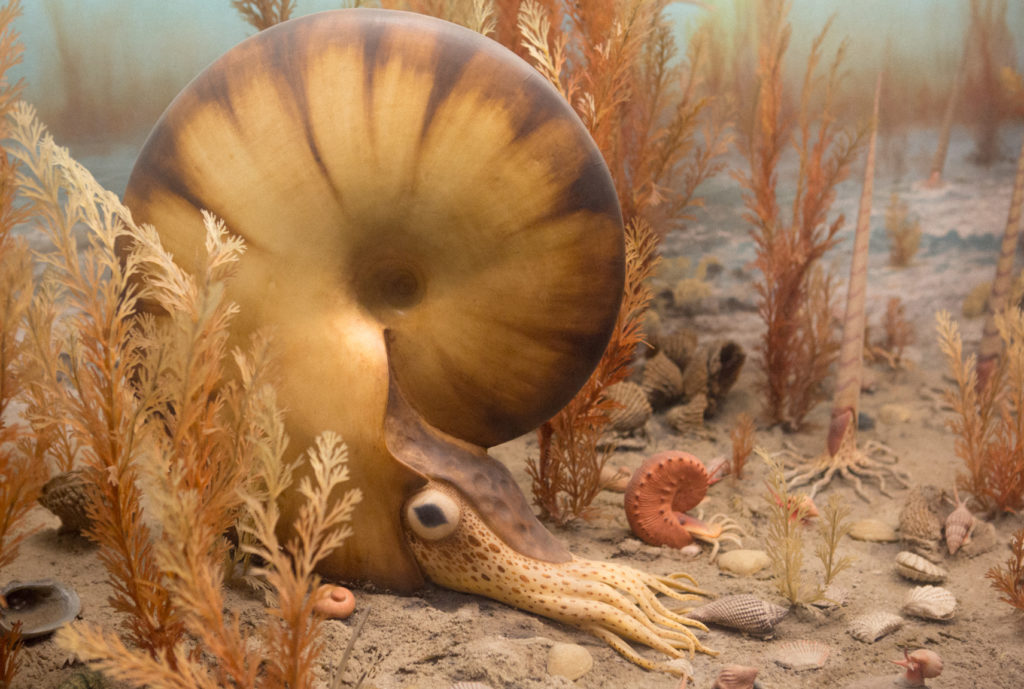 Anelise Chen: Delighting in the Mollusks of Art History
Anelise Chen: Delighting in the Mollusks of Art History
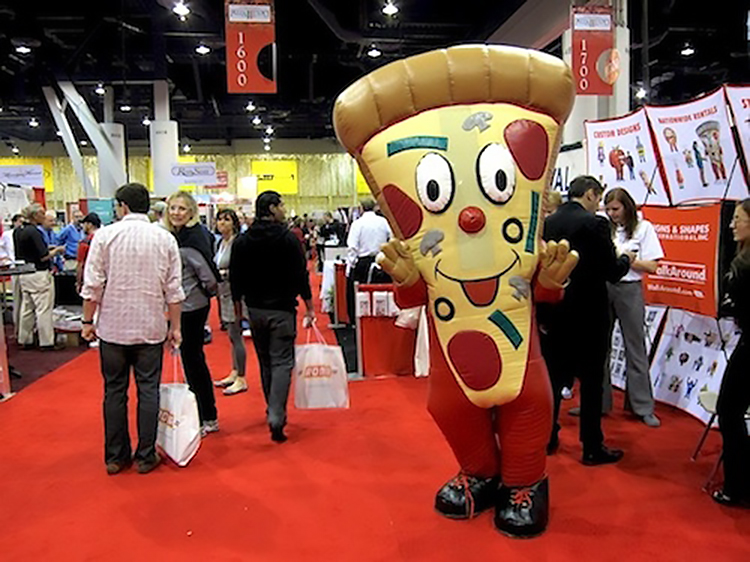 Pizza Complex Las Vegas: At the International Pizza Expo
Pizza Complex Las Vegas: At the International Pizza Expo
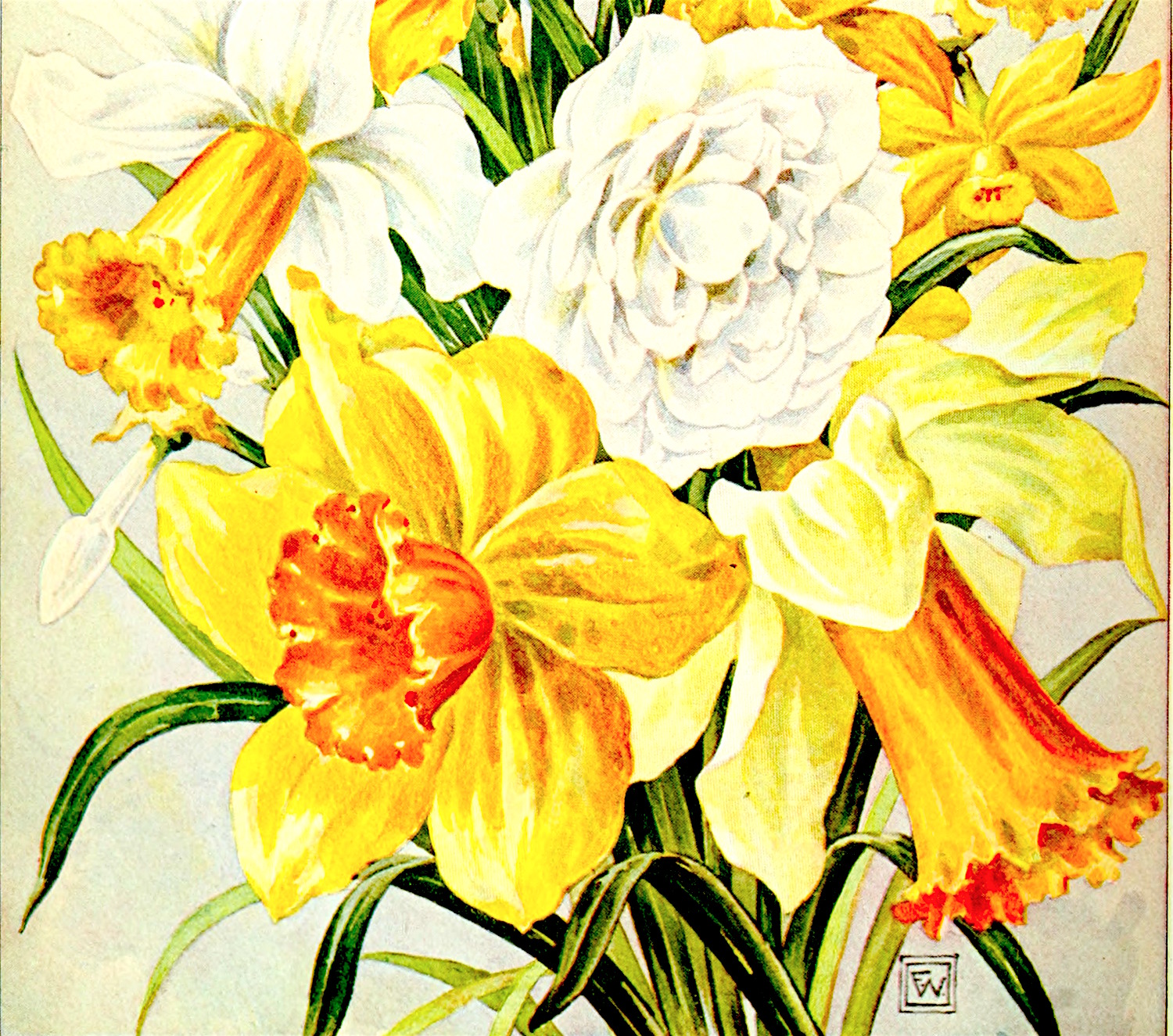 May Swenson’s “Daffodildo,” a Lusty Poem for May
May Swenson’s “Daffodildo,” a Lusty Poem for May
 Whale Vomit Episode 5: Startup Monarchy
Whale Vomit Episode 5: Startup Monarchy
 How to watch the Texas vs. TCU football without cable: kickoff time, streaming deals, and more
How to watch the Texas vs. TCU football without cable: kickoff time, streaming deals, and more
 Your iPhone has built
Your iPhone has built
 Elias Sime’s Art Repurposes Electronic Waste from Abbis Ababa
Elias Sime’s Art Repurposes Electronic Waste from Abbis Ababa
 SpaceX's Starlink satellite launch in pictures
SpaceX's Starlink satellite launch in pictures
 ¡Figaro! 90210, a New Adaptation, Takes Immigrants’ Rights to the Opera
¡Figaro! 90210, a New Adaptation, Takes Immigrants’ Rights to the Opera
HBO Max’s ‘Love Life’ justifies its existence in Season 2'Ghostbusters: Afterlife' is a soulless ode to nepotismTrick or treat with UNICEF and help vaccine outreachAdobe announces big updates to Photoshop, Illustrator, and moreGrandpa Biden and Trump fighting memes are the only thing that can save AmericaLindsay Lohan has a bizarre new gig with Lawyer.comThe 9 best crime shows on Peacock for when you want to be a detectiveWhat is a VPN Router?'Eternals' brings great new heroes to the MCU but leaves us wondering whyAdobe announces big updates to Photoshop, Illustrator, and moreEveryone calm down about Chris Evans' moustache for a secondHenry Cavill pays tribute to his moustache in a glorious Instagram videoNASA's Mars rover is back in action after two weeks of silenceWhat the giant James Webb telescope will see that Hubble can'tFox News analyst quits after finally realizing it's a 'propaganda machine'5 damning revelations from the Facebook PapersThe most exclusive 'dating app for Jews' is not actually that JewishGrown man Ben Carson blames his wife for the $31,000 dining room setAdobe announces big updates to Photoshop, Illustrator, and moreHow 'Dune' the movie differs from the book Ariana Grande is back home in Florida, but her touring plans are still unclear Unexpected video game horses, ranked 'Star Wars' turns 40: Looking back at the (mostly glowing) reviews from 1977 'Game of Thrones' fans are all making the same joke about the Mountain Sansa is the Stark you should be watching in the 'Game of Thrones' trailer DJI Spark drone is so small and smart, it could be a game News anchor saves the day when meteorologist's earring pops off during broadcast J.K. Rowling slams Fox contributor in the wake of the Manchester attack IFTTT wants to connect all those companies and their connected devices This photo of Carrie Fisher and Billie Lourd in 'Star Wars' costumes will ruin you Mark Zuckerberg awkwardly takes us inside his Harvard dorm room on Facebook Live Regulators in the Philippines want to ban rosaries on dashboards and people are pissed The NFL just did something awesome and unexpected, really, we're not kidding Sean Hannity is desperate for your retweets A full breakdown of that battle map in the 'Game of Thrones' Season 7 trailer Facebook's Trending Topics now offer you a choice of what publisher you want to read Xiaomi's Mi Max 2 promises the holy grail of smartphone battery life New video shows a 'dummy' iPhone 8 in all its glory Emojipedia will let you track the popularity of your favorite emoji Instagram's new 'archive' feature lets you hide posts without deleting
2.0748s , 10156.421875 kb
Copyright © 2025 Powered by 【Deborah Driggs Archives】,New Knowledge Information Network